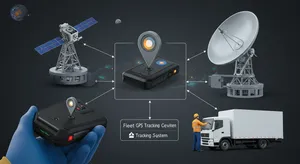
GPS Technology Components
- GPS satellites orbiting at 20,200 kilometers altitude broadcasting precise signals
- Minimum four satellite signals required for accurate position determination
- Atomic clocks in satellites providing nanosecond timing accuracy
- Trilateration calculations determining exact vehicle coordinates
- Signal processing algorithms compensating for atmospheric interference
- Continuous signal reception enabling real-time location tracking
- Backup positioning systems including GLONASS and Galileo satellites
- Ground-based correction systems improving accuracy to within 3 meters